All over the world, project managers would unanimously agree that estimating is the most challenging part of project management. Estimating in the world of business and project management is the art of predicting the number, value, quantity, or extent of resources needed to complete a project.
Key Takeaways
- 01Analogous estimating helps you validate your feasibility study throughout a project's lifecycle
- 02Analogous estimating is helpful when you have little or no data points from past projects but need to draft quick estimates
As a project manager, the right estimating process is the key to accurate results. Most projects get shut down even before they see the light of day, while others stop midway owing to estimate errors.
With several available estimating techniques, choosing a suitable method becomes tricky for project managers, which is how analogous estimating saves the day. Here's all you need to know about analogous estimates as a project manager.
Table of Content
- What is Analogous Estimating?
- Historical Context and Development
- The Importance of Analogous Estimating in Project Management
- When and How to Use Analogous Estimating?
- 5 Steps to Implement Analogous Estimating
- Real-World Applications and Case Studies
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Analogous Estimating?
Analogous estimating is a top-down estimation method that involves comparing past projects with current projects to estimate significant parameters such as time and cost.
Let's say you're working on a new project but had worked on a similar project a while back. You had done a lot of research on the past project and prepared the quotes, invoices, resource allocation sheet, as well as the project scope.
Instead of doing a lot of guesswork, you then decide to use the previous project's data to build your estimate for the current project. As a result, you could easily approximate the cost, project resources, and project duration for the new project.
This technique relies on historical data from previous projects, making it an efficient approach for generating quick estimates during the early stages of project planning.
Definition and core principles
Project managers use analogous estimating techniques to predict the cost and duration of new projects where there are similarities with past ones. In the example above, you used the data from the previous project to create variables that helped with the estimation. This technique is known as analogous estimating and involves analyzing all previous project data and building an analogy for the current project.
- Absolute value
- Ratio estimates
- Three-point estimates
- A range
Historical Context and Development
The evolution of analogous estimating is majorly interrelated with the development of modern project management practices in the United States. Below is a timeline highlighting its milestones within the U.S. context:
Evolution of Analogous Estimating in the U.S.
| Year | Milestone | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1950s | Emergence in large-scale projects | Analogous estimating became popular in large-scale engineering and defense projects. For which historical data proved useful for forecasting costs and timelines. |
| 1969 | Development of the PRICE system | Frank Freiman at RCA introduced the Programmed Review of Information for Costing and Evaluation (PRICE) system, using historical data for parametric cost modeling. |
| 1980s | Adoption in PMI's PMBOK Guide | Project Management Institute (PMI) incorporated analogous estimating into its PMBOK Guide. This establishes a standard project management estimation technique. |
| 2000s | Broad adoption across industries | The technique gained widespread use in IT, construction, and software development projects. This helps in early project planning. |
| Present | Enhanced through digital tools | Modern project management software is automated to get data-driven analogous estimating. |
The Importance of Analogous Estimating in Project Management
Analogous estimating plays a vital role in project management to aim for success. It aids project managers in making informed decisions during the initiation phase and saves time and effort.
Here's why it is important:
1. Early-stage planning
- Quick decision-making: Provides rough estimates for costs, timelines, or resources when detailed project data is not yet available.
- Project kick-start: Helps teams and stakeholders start work faster by offering initial projections.
2. Resource allocation
- Budget planning: Guides initial budget estimates to avoid over- or under-allocating funds.
- Time management: Establishes baseline timelines for effective scheduling.
- Resource optimization: Allocates manpower and materials based on historical patterns.
3. Cross-industry applications
- IT projects: Quickly estimate development timelines to help teams plan.
- Construction: Predicts labor and material costs using data from similar builds.
- Healthcare: Streamlines project proposals for new facilities or equipment installations.
4. Case studies and supporting data
- PMI study: 60% of successful projects use historical data to enhance estimation accuracy.
- IT Industry example: Analogous estimating shortened planning phases by 30% for agile teams, enabling faster project launches.
- Construction insight: Historical data improved cost predictability, reducing budget overruns by 15% on average.
Benefits of analogous estimating
Here are some of the benefits of using analogous estimating as a project manager:
Limitations and considerations
- Analogous estimation functions on the premise that variables such as labor costs and resources remain constant. With economic factors like inflation, estimates could be quite inaccurate.
- Analogous estimating is not as accurate as other estimating techniques and should be avoided for large or complex projects.
- Analogous estimation is better for determining cost estimates at the early stages of a project and should only be used where there is limited data about a project.
When and How to Use Analogous Estimating?
Since analogous estimates work with previous data, analogous estimating techniques can only be applied where you have sufficient data from a similar past project. If you don't have sufficient data points or haven't done any projects that can serve as a reference point, you should avoid using this estimating technique. Here are scenarios where analogous estimating fits in perfectly:
1. Early-stage estimations
You can employ analogous estimation when conducting a project feasibility study, even before you determine the required resources or complete scope of the project. Analogous estimation helps you decide whether future projects will be profitable before you decide to bid for them.
2. Insufficient project details
You might use analogous estimation if you have insufficient or inconclusive data on a current project but need to determine whether a project is worthwhile.
3. Quick estimate
An analogous estimate might be the best option where you need a rough estimate if you're bidding on a project. With a little research, it is possible to make close assumptions about the total cost and likely duration of a project.
4. Expert insight
Most project managers utilize their wealth of knowledge and experience from previous projects to make analogous estimates where there are similarities with previous projects.
5. Dealing with limited project data
You should use analogous estimation if you have very little data or previous experience to make a conclusive cost or project requirement comparison but still need to create an estimate.
5 Steps to Implement Analogous Estimating
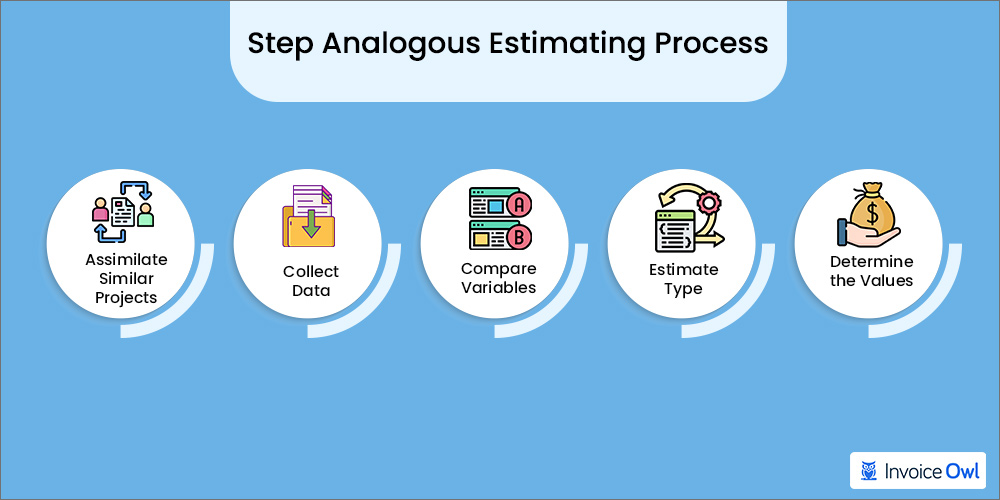
If you plan to use analogous estimating for your next project, here is the step-by-step process you should follow.
Step 1: Identifying comparable projects
You or your team may have drafted an estimate for a similar project in the past so ensure you pour over your project database to find references to them. If you find any useful data on any similar historical project, you could use that to estimate the timeline and cost for any given project.
Step 2: Data collection and analysis
The next step is to collate all the data you've found relating to a past project, including costs, resources, and timeline. You could also do some online research on similar projects and aggregate your findings before you move ahead with the estimation process.
Step 3: Comparing project variables
While the two projects could be similar, they may differ on many levels. Ensure you identify the comparable variables for both projects before proceeding with your estimation.
Step 4: Determining the estimate type
By now, you should have an idea of which analogous estimating process works best for your project case. A single-point estimate is preferred for simple projects, while you should use an estimated range when there are variabilities in the project.
A ratio estimate is preferred when you need to establish how two variables relate to each other. A three-point estimate helps you better understand the risks of any project by generating three different estimates: an optimistic estimate, a pessimistic estimate, and a realistic estimate.
Step 5: Developing estimation values
Once you have arrived at the most suitable approach, apply it to determine a project's risk, project cost, and profitability margin.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
There are many scenarios where you can use analogous estimating on a current project. It is important to note that technique can also be applied in cases where you have little or no experience on a similar past project.
Case Study: Residential construction projects
Say you were working on a current project to build 10 houses in a community. If you are working in an agency, you can always ask people who have worked on similar past projects for data. They will provide you with estimates of the overall project, as well as the project scope and requirements. You can use this data to create accurate estimates while choosing the variables that fit your needs.
While working on a project estimation, you can use clients' historical information to learn more about their preferences while drafting an estimate. Analogous estimation techniques can also be employed when the project requirements or scope is unclear.
Create Lightning-Fast Estimates and Invoices With InvoiceOwl
InvoiceOwl is a better way to create and send quick estimates and invoices to your clients.
Get Started Now!Conclusion
The analogous estimating technique is a top-down approach that works best in project validation, project scope optimization, and project scope building. This project estimation method is helpful for contractors and handypersons asked to bid on a project they might have little experience with. It helps build an analogy using the variables from past projects to help you create an estimate for current projects.
If you send out lots of estimates, invest in a reliable estimate software like InvoiceOwl that helps you create and send accurate estimates and invoices in just a few clicks. With an intuitive user interface and simple workflows, InvoiceOwl makes it easy for anyone without accounting experience to manage their business finances efficiently.
Want to see how easy it is to create and send estimates and invoices? START Your FREE Trial today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Analogous estimating uses historical data from similar projects in the past. It provides quick, high-level estimates based on expert judgment. It is a less precise method but faster. On the other hand, parametric estimating considers the statistical relationships or unit-based metrics such as cost-per-square foot. This offers greater accuracy but you need reliable data. The parametric method is suitable for detailed planning with measurable inputs.
Analogous estimating is used across numerous industries including software development, manufacturing, and construction for early-stage planning. In software development, it predicts development efforts based on comparable applications. The manufacturing industry uses it to estimate production timelines for similar products. It is even applicable in event planning as it assesses budgets and schedules for recurring events.