Understanding journal entries for invoices will help you keep your financial records accurate. But we understand that maintaining a tidy financial record can be quite overwhelming, especially for beginners.
So here's how to record invoices in accounting. Today, we will explore basic terms related to accounting, ways of recording, and more. So let's begin.
Key Points You'll Learn
- 01The difference between accounts payable and accounts receivable
- 02Common ways financial transactions are recorded in accounting
- 03Step-by-step accounts payable process for recording invoices
- 04Features of a functional accounts payable system
- 05Best practices to improve your invoice recording process
Accounts Payable vs. Accounts Receivable
Every transaction creates both accounts payable and accounts receivable for the customer and the vendor, respectively. So to get a better understanding, let's discuss what Accounts Payable and Accounts Receivable are and the difference between them.
- Accounts payable
Commonly referred to as AP, it is basically the money an organization owes third-party suppliers or creditors.
- Accounts receivable
Accounts receivable are outstanding invoices of payments due to you by customers for the purchase of goods or services. It is referred to by its short form, AR.

Here are the differences between them:
Accounts Payable vs. Accounts Receivable Comparison
| No. | Accounts Payable | Accounts Receivable |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | It is the money you owe to other businesses, suppliers, or creditors for any purchased goods or services. | It is the money others owe to you for any purchased goods or services. |
| 2. | It depicts a current liability. | It depicts a current asset. |
| 3. | It is a cash outflow. | It is a cash inflow. |
| 4. | It consists of vendors' records. | It consists of clients' records. |
Commons Ways Financial Transactions Are Recorded in Accounting
Businesses engage in many transactions and need a distinct set of journal entries. Therefore, they customize their invoice recording process as per their needs. Here are a few ways most businesses record their financial transactions.
1. Revenue journal entries
For many businesses, their revenue journal entry can be split into two main categories: sales accounts and allowance for doubtful accounts.
- Sales accounts: When businesses make a sale, the corresponding journal entry credits the sales account and debits the accounts receivable.
- Allowance for doubtful accounts: In business, there are times when customers are unable to pay for sales made on credit. In these situations, a slight adjustment is made to debit the bad debt expense account to credit the allowance for doubtful accounts.
When the customer pays later, the entry can be reversed by entering the debit amount as the accounts receivable and crediting the bad debt expense. You can then issue a receipt to the customer by debiting the cash account and crediting the accounts receivable.
2. Expense journal entries
- Accounts payable journal entry: This refers to the amount payable in journal entries for an expense on credit for goods or services. This account is debited when payments are made.
- Payroll journal entry: A payroll journal entry is a recording of the compensation or wages due to employees or contractors. Although it's a bit more complicated due to taxes, you will still debit the expense account and credit the cash account.
- Petty cash journal entry: A petty cash journal entry creates a debit to the petty cash account and a credit to the regular cash account.
- Depreciation recording: A journal entry for depreciation is issued by debiting the depreciation expense account and crediting the accumulated depreciation account.
- Accrued expense recording: Accrued expenses or liabilities are unpaid expenses during an accounting period. The relevant expenditure account is debited, and the accrued expense account is credited.
3. Asset journal entries
- Cash reconciliation journal entry: Banks typically accumulate charges they've not reconciled. For cash reconciliation journal entries, simply debit accounts such as Bank Service Charges and credit Cash. For a journal entry when a customer's check could not be processed due to insufficient funds, debit accounts receivable and credit Cash.
- Disposal of assets journal entry: When an asset is fully depreciated, its accumulated depreciation account will be debited as a single entry in the general journal, and the relevant asset account is credited. This may result in a loss or gain in some instances.
- Fixed asset journal entry: When buying a fixed asset on credit, the applicable asset account will be debited, and the account payable will be credited. Fixed assets bought in installments usually include the interest rate.
- Prepaid expense adjustment journal entry: Prepaid expenses are regarded as assets since they offer future economic benefits to an organization. In this case, the appropriate debit account is debited, and a credit to cash or the relevant expense account is made.
4. Liability journal entries
For owed expenses, the applicable expense account will be debited by the appropriate debit amount while the cash or accrued liability account will be credited.
5. Equity journal entries
- Stock repurchase journal entry: When Companies can record a journal entry for the repurchase of their stock by debiting the treasury stock account and crediting the cash account.
- Dividend journal entry: When recognizing a liability to pay dividends, the retained earnings account gets debited while the dividends payable have credit amounts recorded. After the dividends are paid, the entries get reversed and the dividends payable account is debited while there is a credit entry made in the cash account.
The Account Payable Process
The accounts payable process in an organization is the management of its short-term payment obligations and covers everything from paying vendors and suppliers for goods and services purchased to managing and verifying incoming bills and invoices.
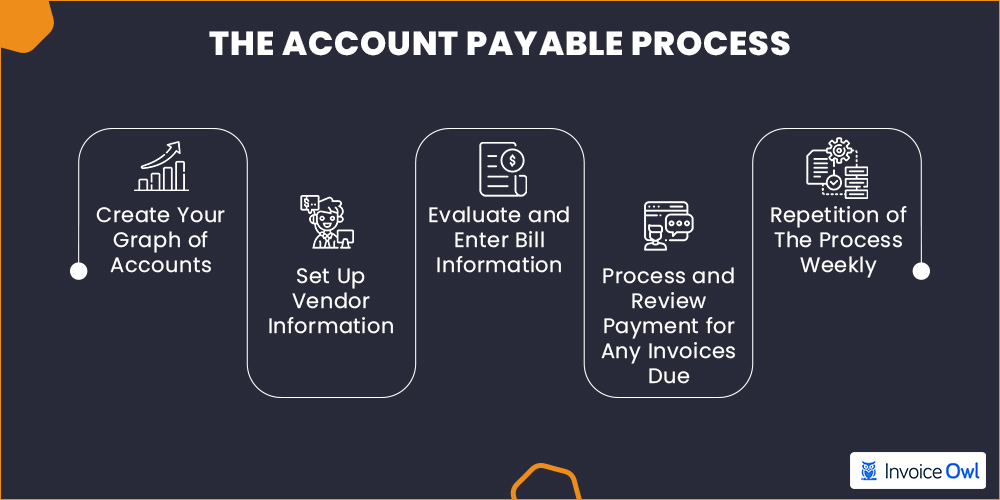
For most organizations, the accounts payable process can be split into four steps:
Features of a Functional Accounts Payable System
Having an accurate account payable is not only essential to producing an accurate balance sheet, but it also indicates whether you are overspending or relying too much on credit. Also, a decrease in accounts payable indicates negative cash flow, which can help you detect an inventory that could be tying up cash in your bank account.
Regardless of the company's size, the accounts payable would only pay invoices and bills that are accurate and legitimate. So before an invoice is entered into your accounting records, the invoice must clearly itemize what was ordered, what has been received as well as the unit and total costs.
Most organizations employ safeguards like using invoicing software to ensure all vendor invoices are accounted for and to prevent:
- Paying a fraudulent invoice
- Paying an invoice twice
- Paying an inaccurate invoice
Here are a few features of a functional accounts payable process:
How to Improve Your Accounts Payable Process
Without optimizing your accounts payable system, you end up stalling the growth of your business. Here are some of the best practices for AP departments globally.
- Map out your accounts payable process: Create an accurate plan of your current accounts payable process to help quickly identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks.
- Simplify workflow: Identify redundancies and adopt a more streamlined approach with clearly defined processes.
- Avoid paper invoices: Asides from the cost of printing numerous invoices, it takes a bit of time to manually transfer invoices to the appropriate department for verification and authorization. Hinting your suppliers or vendors about switching to an app like InvoiceOwl to send electronic invoices would ensure you don't lose track of them and avoid late payments.
Here is our guide on how you can digitalize your invoices.
Ready to Streamline Your Invoice Recording?
Join 100,000+ contractors using InvoiceOwl to create professional invoices and automate your accounting workflows.
Try Free for 3 DaysFrequently Asked Questions
Invoices sent to customers are recorded as journal entries in the accounting journal. The journal entry is recorded by entering the total amount due from the invoice as a debit on accounts receivable and a credit on the sales account.
The accounts payable are expenses or payments to be paid. Therefore, to make the journal entry, you need to debit the expense or asset of the related purchase and credit the accounts payable account.
Once the accounts payable process is complete, a debit entry is made to the accounts payable, and a credit entry is made to cash.
Recording invoices has the following benefits:
- It helps you keep track of your expenses and income.
- It facilitates getting paid and paying others on time.
- It eases legal matters such as tax.
No, the accounts payable are considered a current liability on the balance sheet as they constitute payments owed to vendors or suppliers. Accounts receivable on the other hand, fall under the category of the asset as it constitutes the money given on credit to the customers with a promise to be received in the future.
Conclusion
Recording an invoice is a tiresome process. This is why most growing organizations hire an accountant. And even with the perfect general ledger recording process, there could be lots of errors.
When running a business where multiple transactions are happening simultaneously, these errors can cost you a fortune which is why many organizations use accounting software that can be tailored to their operations.
InvoiceOwl helps small businesses manage their income and streamline their bookkeeping process. Create multiple types of invoices online and manage your clients effortlessly. With the power of cloud computing, bookkeeping has never been easier.
Try Invoice Owl for FREE to create professional invoices and collect payments online.