Ever wondered how businesses make sure their goods reach international destinations without delays? The answer lies in the shipping invoice. It is one of the most important documents that bridges the gap between logistics, payments, and customs compliance.
In this blog, we are going to focus on shipping invoice meaning, its importance for international trade, and steps to create the perfect shipping invoice.
Let's start.
Key Takeaways
- 01A shipping invoice (bill of lading) is a legal document between shipper and carrier that governs international trade
- 02Essential components include contact information, shipment details, reference numbers, and authorized signatures
- 03Different types exist including commercial, proforma, consular, and customs invoices for various purposes
- 04Shipping invoices serve as evidence of contract, receipt of goods, and document of title
- 05Proper documentation ensures customs clearance, trade finance facilitation, and smooth delivery
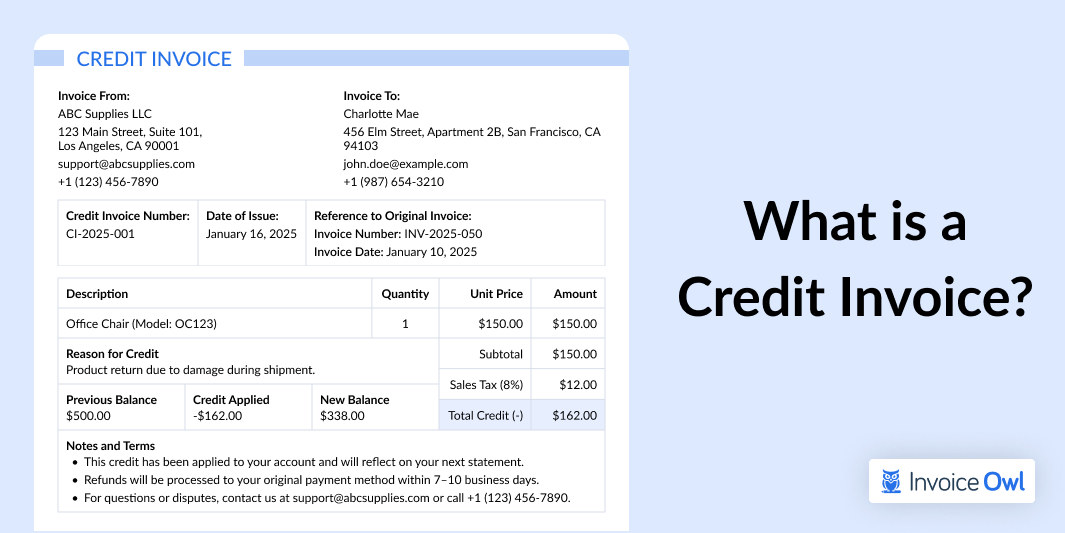
What is Bills of Lading?
A bill of lading is a legal document associated with freight stating the agreement between the shipper and the carrier. It comprises important details of the cargo in shipment and gives ownership to the receiving party specified on the document. Also, known as shipping invoice is a document used in international trade
This document covers the type of goods being transported by trucking companies, product name, quantity (volume), rate per quantity, total costs involved, and the business terms. Last but not least, it governs the relationship between the shipper and carrier while transporting the goods.
Essential Components of a Shipping Invoice
As a vital instrument in the transportation of goods across borders, the bill of lading must accurately reflect the details of the shipment. To facilitate a seamless shipping process, make sure your bill of lading includes the following 10 crucial elements.
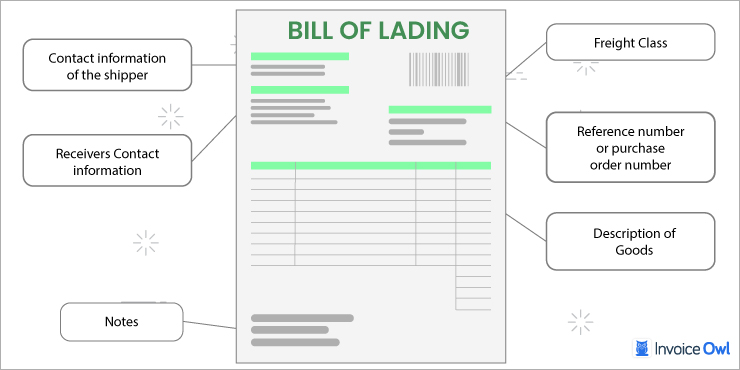
1. Contact information of the shipper
The first thing to appear in the bill of lading is the shipper's information; it included the invoice number, full company name, logo, business address, and phone number or fax number.
2. Receiver's contact information
After including the shipper's information in the invoice, also add that of the receiver. It must include every detail of the receiver with the full company name or contact person information, logo, business address, and phone number or fax number. When creating an invoice, it is important to ensure your invoicing software supports international addresses.
3. Reference number or purchase order number
The purchase order number and other useful figures for referencing the bill of lading must be added to validate the document and to keep a record. The freight shipping invoice may also require these numbers before releasing the items.
4. Additional instructions or notes
A section on the bill of lading allows the inclusion of special notes to the carrier about the shipment taking place.
5. Pick-up date
The date of pick up should be noted on the bill of lading to affirm when the shipment was received by the carrier. This data is used for tracking a shipment and is needed during invoice reconciliation.
6. Description of goods
The goods in the shipment have to be described as they are on the bill of lading or as discussed during product requirements. The description for billing purposes includes the quantity of the items, weight, value, and measurement if applicable.
7. Type of packaging
A bill of lading must list the type of materials used in packaging the shipment, maybe cartons, pallets, crates, or drums.
8. Freight class
It is important to tick what class of freight your shipment is, classes of freight are up to 18. For proper identification based on factors like value and dimension, state the class of freight on the bill of lading.
9. Special designations
Sometimes, the goods that are being shipped may need extra care or have to be handled with ease. Whatever the case is, you must state any special designation. For example, the shipment may be hazardous if brought near some substance. State what has to be done to avoid danger.
10. Authorized signature
The bill of lading once signed by an authorized representative of the shipping company, serves as a confirming acceptance of the goods for shipment. The signature indicates that the terms and conditions outlined in the bill of lading have been acknowledged and signify agreement to the terms of carriage.
Custom Compliance Checklist
Make sure to download and refer to this regularly to ensure your shipments meet all the necessary customs requirements and regulations.
Purpose and Benefits
Bill of lading or shipping invoices are generally issued for the following purpose or objectives:
1. As evidence of the contract of carriage
A bill of lading serves as evidence of the contract between the shipper (seller/exporter) and the carrier (shipping company) for the transportation of goods. It outlines the terms and conditions of the shipment, such as the parties involved, the goods being transported, and the destination.
2. For receipt of goods
When the carrier receives the goods from the shipper, the bill of lading acts as an acknowledgment. It represents that the carrier has taken possession of the goods in the described condition and quantity. This helps ensure clarity and reduces the chances of disputes.
3. Acknowledged as a document of title
A bill of lading is a transferable document to a third party. It can be anyone such as a bank or the consignee (buyer/importer), giving them the right to receive the goods. The party in possession of the bill of lading is entitled to claim the goods from the carrier at the destination. This contract specifies the terms and conditions of the shipment, including the responsibilities of each party.
4. Can be used as instructions for delivery
The bill of lading provides clear instructions for the carrier on where and to whom the goods should be delivered. It specifies the consignee and the destination port or location. Hence, to streamline the process, many businesses and logistics providers utilize readymade and easily downloadable free invoicing templates.
5. For facilitating trade finance
In international trade, the bill of lading is often used as collateral for trade financing, such as letters of credit. Banks may require the presentation of the bill of lading before releasing payment to the seller/exporter.
6. For customs clearance
The bill of lading is an essential document for customs clearance at the destination port or country. Customs authorities may require the original bill of lading to verify the shipment details and assess any applicable duties or taxes.
Ditch the guesswork! This free currency calculator tool keeps your international finances on fleek. Effortlessly calculate shipping costs and invoice amounts in different currencies, ensuring accurate pricing for your international transactions.
Types of Shipping Invoices
There are several types of shipping invoices used in international trade, depending on the mode of transportation and the specific requirements of the parties involved. Here are some common types of shipping invoices:
1. Commercial invoice
- These invoices are one of the most familiar and widely used invoices for any mode of transportation (sea, air, or land).
- It provides detailed information about the goods being shipped, including their description, quantity, value, and other relevant details.
- It serves as a key document for customs clearance and is used to calculate applicable duties and taxes.
- Learn more about the commercial invoice.
2. Proforma invoice
- A proforma invoice is issued before the actual shipment takes place and serves as a preliminary invoice or quotation.
- It provides an estimate of the goods' value, shipping costs, and other charges, allowing the buyer to secure funds or obtain necessary documentation.
- Proforma invoices are often used in international trade to facilitate the opening of letters of credit or obtain import licenses.
- Learn the difference between a commercial invoice and a proforma invoice.
3. Consular invoice
- A consular invoice is a specific type of invoice required by some countries for customs clearance purposes.
- It must be certified or legalized by the consulate or embassy of the destination country before the goods can be exported.
- Consular invoices typically provide more detailed information about the shipment, such as the country of origin, HS codes, and the signatures of authorized parties.
4. Customs invoice
- Some countries may require a separate customs invoice in addition to the commercial invoice.
- A customs invoice is specifically designed to meet the requirements of the destination country's customs authorities and may include additional information or formats.
- It is often used for statistical purposes and to facilitate the calculation of applicable duties and taxes.
5. Packing list
- While not a true invoice, a packing list is a document that accompanies the shipment and provides a detailed list of the contents of each package or container.
- It includes information such as the quantity, weight, and dimensions of the items being shipped.
- Packing lists are used by customs officials and carriers to verify the contents of the shipment and ensure accurate handling and delivery.
These are just a few examples of the various types of shipping invoices used in international trade. The specific type of invoice required may vary depending on the destination country, mode of transportation, and the nature of the goods being shipped. It is essential to consult with shipping experts or local customs authorities to ensure compliance with the appropriate documentation requirements.
7 Steps to Generate a Shipping Invoice
Here are seven steps to create a shipping invoice that consists of all the important details to make it a valid one.
Step 1: Download a customizable template
Create your customized invoice from scratch or the existing one. Many inventory solutions offer customized templates. Once customized, it becomes easy to create future invoices by filling up essential details.
Step 2: Add the buyer and seller's information
After downloading the invoice template, start adding the important information. This information comprises important details like seller and buyer information like their name, contact details, email address, shipping address, etc.
Step 3: Include shipment information
Ensure to add shipping information like the date, time, location, and destination. Don't forget to add the invoice number as it helps in tracking the package. An invoice number has to be unique and different from other package units. To make this happen, use sequential numbers for your invoices.
Step 4: Mention customer reference number
Add a customer reference number which helps the buyer to track their order status, arrange returns, and ask their queries– are some of the most important aspects of managing clients.
Step 5: Add terms and conditions of payment
Mention the important information related to payment terms and conditions. This section states that both sellers and buyers have agreed on the payment terms. Add various payment methods like cash, card, or net banking to your invoice.
Step 6: List shipment items
Add a detailed description of every single thing included in the shipment. This description comprises the weight, per-unit prices, and product quantity. Making a proper list of the orders enables the carrier and buyer to verify the invoice with the goods received.
Step 7: Provide price information
Last but not least, mention the final amount of shipment and the commercial value. If there are any additional charges, make sure to add them to your calculation to realize the final value.
Shipping Invoice Template (Free)
To simplify your shipping process and help you generate shipping invoices instantly, we offer a free, ready-to-use template. All you need to do is fill in the shipment details, add the sender and receiver information, include any shipping costs or surcharges, and customize it with your company logo and brand name.
Download FREE Shipping Invoice Template
Get a professional, customizable shipping invoice template that helps you create accurate invoices in minutes.
Download TemplateShipping Invoice vs Commercial Invoice
It is essential to understand the difference between a shipping invoice and a commercial invoice for businesses involved in internal trade and logistics. Here is a detailed table showcasing their different purposes in the business.
Shipping Invoice vs Commercial Invoice
| Aspect | Shipping Invoice | Commercial Invoice |
|---|---|---|
| Primary use | To bill for shipping services and provide a record of transportation costs. | To declare goods for customs clearance and provide proof of the transaction. |
| Customs role | Focuses solely on shipping and delivery charges. | Required for customs clearance; determines import/export restrictions. |
| Regulatory requirements | Not governed by international trade laws but follows shipping industry standards. | Must comply with international trade regulations, including INCOTERMS and customs documentation rules. |
| Time of issue | Issued after the shipment is completed. | Issued at the time of sale or before goods are shipped. |
"Sunny Trends," a small business in Los Angeles, sold 100 handcrafted soy candles to a New York boutique for $1,000. The shipping invoice included $100 for shipping, $160 in sales tax, and detailed the FedEx carrier, tracking number, and 5-day delivery timeline. The total amounted to $1,260, with clear itemization for easy verification.
The Final Words
After delving into this comprehensive guide on shipping invoices, we've navigated you through the intricate world of international trade documentation, shedding light on the pivotal role that invoices of shipment play in facilitating seamless transactions.
Lastly, we suggest you apply the knowledge gained here to optimize your invoicing processes, enhance your business practices, and unlock the full potential of your global trade.
Want to Simplify Your Shipping Invoices?
Try InvoiceOwl to create, edit, and download professional invoices instantly. Save your time and streamline your invoicing process today!
Try Shipping Invoice GeneratorFrequently Asked Questions
Yes, you need both invoices for international trade as every document serves their unique purpose. The shipping invoices are focused on transportation costs whereas the commercial invoice is important for customs clearance and duty assessments.
Accurate product descriptions and Harmonized System (HS) codes are crucial for proper customs clearance and duty calculations. To ensure accuracy, you should consult official product classification resources, such as the Harmonized Tariff Schedule or online HS code databases.
A shipping invoice is crucial for customs clearance, payment processing, and ensuring compliance with trade regulations. It serves as a commercial document detailing the transaction between the buyer and seller.
The shipping invoice is issued by the seller (exporter or shipper) to the buyer (importer or consignee).
No, shipping invoices are primarily used for international shipments involving cross-border transportation of goods. However, some businesses may choose to use them for domestic shipments as well.
A shipping invoice and a sales invoice differ in their purposes. A shipping invoice mentions the freight charges and transportation costs, whereas a sales invoice covers the products or services, unit price, and payment terms. A sales invoice is directly related to the sale transactions and not the shipment.